


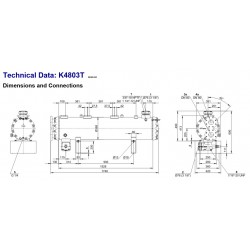

Adatto per refrigeranti standard, incluso. HFO, R290 e R1270.
Condensatore a fascio tubiero con tubi alettati e riempimento con gas di protezione.
La pressione massima di esercizio è di 33 bar.
staffe di montaggio in basso e in alto per un compressore tandem

EXPERT ADVICE
Professionals in refrigeration technology
SINCE 1986
Since 1986 in refrigeration technology

FACTORY GUARANTEE
You have Always genuine manufacturer's warranty
CUSTOMER SERVICE
info@mfmref.com
Suitable for standard refrigerants.
Shell and Tube condenser with finned pipes, protective gas charge, entrance.
Rotalock or soldering connection soldering connection, flange with fluid output.
Rotalock valve with solder connection, K123HB.. K4803TB with second fluid output (ships), right angle mounting brackets above and below.
Bitzer K4803T is Suitable for all commonly used refrigerants (HFC, HFO, HFC/HFO blends) and including a version approved for use with hydrocarbons (propane, propylene),
K4803T Bitzer condensers represent a standard and robust solution for all normal and technical water cooled applications.
A Bitzer water-cooled condenser is a type of heat exchanger used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems.
Bitzer is a well-known manufacturer of refrigeration compressors and related components, including condensers.
A water-cooled condenser, as the name suggests, uses water as the cooling medium to remove heat from the refrigerant in a refrigeration or air conditioning system.
It is typically used in situations where air-cooled condensers may not be efficient enough due to high ambient temperatures or limited airflow.
Water-cooled condensers are commonly used in industrial and commercial refrigeration systems.
Here's how a Bitzer water-cooled condenser typically works:
Refrigerant Flow: The hot, high-pressure refrigerant gas from the compressor enters the water-cooled condenser coil.
Heat Exchange: The refrigerant flows through a coil or series of tubes within the condenser. Water is circulated around the outside of these tubes or coils.
As the refrigerant passes through the coil, it releases heat to the surrounding water, causing the refrigerant to condense and change from a high-pressure gas to a high-pressure liquid.
Cooling Water: The cooling water absorbs the heat from the refrigerant, causing its temperature to rise.
This heated water is then pumped to a cooling tower or another heat rejection system, where it is cooled down again before being recirculated through the condenser.
The continuous circulation of water helps maintain the condenser's efficiency.
Condensate Collection: As the refrigerant condenses, it forms a liquid called condensate.
This liquid collects at the bottom of the condenser and is typically drained out of the system.
Bitzer water-cooled condensers, like other condenser units, come in various sizes and configurations to suit different applications.
They are designed to efficiently transfer heat from the refrigerant to the cooling water, helping to maintain the proper operating conditions of the refrigeration or air conditioning system.
Water-cooled condensers are known for their high cooling efficiency, especially in hot climates, but they require a reliable source of cooling water and additional infrastructure, such as cooling towers or water pumps, to operate effectively.
Proper maintenance is also essential to prevent scaling or fouling of the water-side surfaces, which can reduce efficiency.